前言
Hadoop IPC为Hadoop RPC最底层的通讯,涵盖了HDFS各个角色组件的通讯以及Yarn各种组件组件的通讯,Hadoop IPC通讯机制依然
采用了NIO非阻塞的方式实现的.尚未使用Netty作为其RPC调用的过程依赖.该源代码中涉及到了NIO中Selector,ByteBuffer,Channel,
以及阻塞队列,等待和唤醒机制等等.
NIO 知识点回顾
Reactor工作模型
Nio也操作NoBlock IO,即非阻塞的IO,NIO采用了reactor工作模型.
+ 当服务启动的时候Socket会注册到给定的selector上,然后返回SelectionKey,该key代表了channel和selector的映射关系.
+ 如果现在有一个网络连接并且他的OP_ACCEPT事件发生,调用selector.selectKeys(),会得到关于OP_ACCEPT事件的key,然后
分发这个事件,通过key的attachment方法得到附件的对象,这个对象就是一个线程对象,通过该对象可以得到socketChannel
+ 得到客户端的socketchannel 就可以读写客户端的socketchannel,先注册一个SelectionKey.OP_READ读事件。并且当前
的Handler对象附加到key对象上sk.attach(this).
+ 当READ事件发生后,则会通过dispatch(sk);分发,通过Handler的run方法进行具体的IO的读操作.
+ 读完了数据之后,注册OP_WRITE事件sk.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_WRITE).然后当该事件发生后,则分发该事件,
调用Handler的run事件处理IO写操作
NIO重要的概念
- Selector
- Channel
- ByteBuffer
Selector运行单线程处理多个Channel,Channel作为管道可以是双向操作的既可以读也可以写入,ByteBuffer作为数据缓
冲区存放到通道中.
多线程等待唤醒机制
概念
多个线程处理同一个资源的时候,但是处理的任务不同,需要互相协作,典型的案例生产者消费者模型.
Hadoop IPC核心类概况
核心类
- RPC
- Client
- Server
RPC类其中最核心涵盖和JDK的反射&动态代理InvocationHandler执行其他类的功能.
按照指定协议构造客户端的代理对象和服务端通讯。
public static <T> T getProxy(Class<T> protocol,
long clientVersion,
InetSocketAddress addr, Configuration conf)
throws IOException {
return getProtocolProxy(protocol, clientVersion, addr, conf).getProxy();
}
获取协议代理,该协议代理包含与远程服务器的代理连接以及该服务器支持的一组方法。
public static <T> ProtocolProxy<T> getProtocolProxy(Class<T> protocol,
long clientVersion,
InetSocketAddress addr,
UserGroupInformation ticket,
Configuration conf,
SocketFactory factory,
int rpcTimeout,
RetryPolicy connectionRetryPolicy,
AtomicBoolean fallbackToSimpleAuth,
AlignmentContext alignmentContext)
getProtocolEngine(protocol, conf).getProxy其中包含了获取协议引擎目前支持的引擎有WritableRpcEngine,ProtobufRpcEngine引擎.
Server主要涵盖了几大核心内部类包括RpcKindMapValue,RpcCall,Listener,Reader,Responder,Connection,Handler.
RpcKindMapValue和RPC类做关联,Rpc种类包含了WritableRpcEngine,ProtobufRpcEngine,这些引擎和他们的rpcInvoker会放到一个Map 中保存起来.
public static void registerProtocolEngine(RPC.RpcKind rpcKind,
Class<? extends Writable> rpcRequestWrapperClass,
RpcInvoker rpcInvoker) {
RpcKindMapValue old =
rpcKindMap.put(rpcKind, new RpcKindMapValue(rpcRequestWrapperClass, rpcInvoker));
if (old != null) {
rpcKindMap.put(rpcKind, old);
throw new IllegalArgumentException("ReRegistration of rpcKind: " +
rpcKind);
}
if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOG.debug("rpcKind=" + rpcKind +
", rpcRequestWrapperClass=" + rpcRequestWrapperClass +
", rpcInvoker=" + rpcInvoker);
}
}
RpcCall继承自Call是RPC的扩展用于处理请求队列,每一个RpcCall属于某一个连接.RpcCall中包含run方法,run最终调用的是RPC引擎的WritableRpcEngine,ProtobufRpcEngine两种实现.以ProtobufRpcEngine代码为例
public Writable call(RPC.Server server, String connectionProtocolName,
Writable writableRequest, long receiveTime) throws Exception {
RpcProtobufRequest request = (RpcProtobufRequest) writableRequest;
RequestHeaderProto rpcRequest = request.getRequestHeader();\
//从请求中获取执行方法的名字
String methodName = rpcRequest.getMethodName();
//从请求中获取执行类的名字
String declaringClassProtoName =
rpcRequest.getDeclaringClassProtocolName();
//获取协议的版本
long clientVersion = rpcRequest.getClientProtocolVersion();
if (server.verbose)
LOG.info("Call: connectionProtocolName=" + connectionProtocolName +
", method=" + methodName);
ProtoClassProtoImpl protocolImpl = getProtocolImpl(server,
declaringClassProtoName, clientVersion);
BlockingService service = (BlockingService) protocolImpl.protocolImpl;
//获取方法的描述
MethodDescriptor methodDescriptor = service.getDescriptorForType()
.findMethodByName(methodName);
if (methodDescriptor == null) {
String msg = "Unknown method " + methodName + " called on "
+ connectionProtocolName + " protocol.";
LOG.warn(msg);
throw new RpcNoSuchMethodException(msg);
}
//协议类型
Message prototype = service.getRequestPrototype(methodDescriptor);
Message param = request.getValue(prototype);
Message result;
Call currentCall = Server.getCurCall().get();
try {
//RPC的指标数据
server.rpcDetailedMetrics.init(protocolImpl.protocolClass);
currentCallInfo.set(new CallInfo(server, methodName));
currentCall.setDetailedMetricsName(methodName);
//调用阻塞真实的方法
result = service.callBlockingMethod(methodDescriptor, null, param);
// Check if this needs to be a deferred response,
// by checking the ThreadLocal callback being set
if (currentCallback.get() != null) {
currentCall.deferResponse();
currentCallback.set(null);
return null;
}
} catch (ServiceException e) {
Exception exception = (Exception) e.getCause();
currentCall.setDetailedMetricsName(
exception.getClass().getSimpleName());
throw (Exception) e.getCause();
} catch (Exception e) {
currentCall.setDetailedMetricsName(e.getClass().getSimpleName());
throw e;
} finally {
currentCallInfo.set(null);
}
return RpcWritable.wrap(result);
}
}
}
-
Listener顾名思义为监听器,该内部类是一个线程类,用于监听客户端发送的请求,封装请求为Call后,放到Call队列中, 每一个Listener中包含多个Reader,默认是一个Reader,由IPC_SERVER_RPC_READ_THREADS_DEFAULT参数决定Hadoop源码中已经写死,Reader负责封装请求为Call后,放到Call队列中.Listener构造方法中监听客户端的发送的请求并且操作多个Reader线程然后启动Reader线程.
Listener(int port) throws IOException {
address = new InetSocketAddress(bindAddress, port);
acceptChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
acceptChannel.configureBlocking(false);
acceptChannel.setOption(StandardSocketOptions.SO_REUSEADDR, reuseAddr);
// Bind the server socket to the local host and port
bind(acceptChannel.socket(), address, backlogLength, conf, portRangeConfig);
this.listenPort = acceptChannel.socket().getLocalPort();
Thread.currentThread().setName("Listener at " +
bindAddress + "/" + this.listenPort);
selector= Selector.open();
readers = new Reader[readThreads];
for (int i = 0; i < readThreads; i++) {
//循环创建多个Read 然后启动多个线程
Reader reader = new Reader(
"Socket Reader #" + (i + 1) + " for port " + port);
readers[i] = reader;
//核心执行逻辑在Reader线程的run方法中
reader.start();
}
acceptChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
this.setName("IPC Server listener on " + port);
this.setDaemon(true);
this.isOnAuxiliaryPort = false;
}
我们去看Reader类的run方法,接下来是一系列方法调用过程run()=>doRunLoop()=>doRead(key)=>readAndProcess()=>
processOneRpc(requestData)=>processRpcRequest(header, buffer)=>internalQueueCall(call)=>
如下 方法添加到了callqueue队列中,这里使用的是环形队列.
private void internalQueueCall(Call call, boolean blocking)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
try {
if (blocking) {
//如果是阻塞执行put方法
callQueue.put(call);
} else {
//如果是非阻塞执行add方法
callQueue.add(call);
}
long deltaNanos = Time.monotonicNowNanos() - call.timestampNanos;
call.getProcessingDetails().set(Timing.ENQUEUE, deltaNanos,
TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS);
} catch (CallQueueOverflowException cqe) {
rpcMetrics.incrClientBackoff();
// unwrap retriable exception.
throw cqe.getCause();
}
}
Handler线程用来处理队列的call.我们可以查看到run方法中如下代码:
//从队列中pop出去
call = callQueue.take(); // pop the queue; maybe blocked here
startTimeNanos = Time.monotonicNowNanos();
if (alignmentContext != null && call.isCallCoordinated() &&
call.getClientStateId() > alignmentContext.getLastSeenStateId())
Responder也是线程类 他的作用是发送RPC的响应的给客户端.我们查看一下run方法
@Override
public void run() {
LOG.info(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": starting");
SERVER.set(Server.this);
try {
//循环运行处理
doRunLoop();
} finally {
LOG.info("Stopping " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
try {
writeSelector.close();
} catch (IOException ioe) {
LOG.error("Couldn't close write selector in " + Thread.currentThread().getName(), ioe);
}
}
}
接下来是doRunLoop()方法,判断selector是否被注册,如果没有循环取出来所有的selectedKeys,然后遍历所有的selectedKeys,
做异步的写入doAsyncWrite(key).
private void doRunLoop() {
long lastPurgeTimeNanos = 0; // last check for old calls.
while (running) {
try {
waitPending(); // If a channel is being registered, wait.
writeSelector.select(
TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS.toMillis(PURGE_INTERVAL_NANOS));
Iterator<SelectionKey> iter = writeSelector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = iter.next();
iter.remove();
try {
if (key.isWritable()) {
doAsyncWrite(key);
}
} catch (CancelledKeyException cke) {
// something else closed the connection, ex. reader or the
// listener doing an idle scan. ignore it and let them clean
// up
RpcCall call = (RpcCall)key.attachment();
if (call != null) {
LOG.info(Thread.currentThread().getName() +
": connection aborted from " + call.connection);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
LOG.info(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": doAsyncWrite threw exception " + e);
}
}
long nowNanos = Time.monotonicNowNanos();
if (nowNanos < lastPurgeTimeNanos + PURGE_INTERVAL_NANOS) {
continue;
}
lastPurgeTimeNanos = nowNanos;
//
// If there were some calls that have not been sent out for a
// long time, discard them.
//
if(LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOG.debug("Checking for old call responses.");
}
ArrayList<RpcCall> calls;
// get the list of channels from list of keys.
synchronized (writeSelector.keys()) {
calls = new ArrayList<RpcCall>(writeSelector.keys().size());
iter = writeSelector.keys().iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = iter.next();
RpcCall call = (RpcCall)key.attachment();
if (call != null && key.channel() == call.connection.channel) {
calls.add(call);
}
}
}
for (RpcCall call : calls) {
doPurge(call, nowNanos);
}
} catch (OutOfMemoryError e) {
//
// we can run out of memory if we have too many threads
// log the event and sleep for a minute and give
// some thread(s) a chance to finish
//
LOG.warn("Out of Memory in server select", e);
try { Thread.sleep(60000); } catch (Exception ie) {}
} catch (Exception e) {
LOG.warn("Exception in Responder", e);
}
}
}
- 最后提到的是
Connection也是Server类的内部类,其中一个Connection包括多个RpcCall.
最后Client类笔者不再做出具体的分析,感兴趣的读者可以下载源代码阅读.
整体流程结构图
整体流程图如下
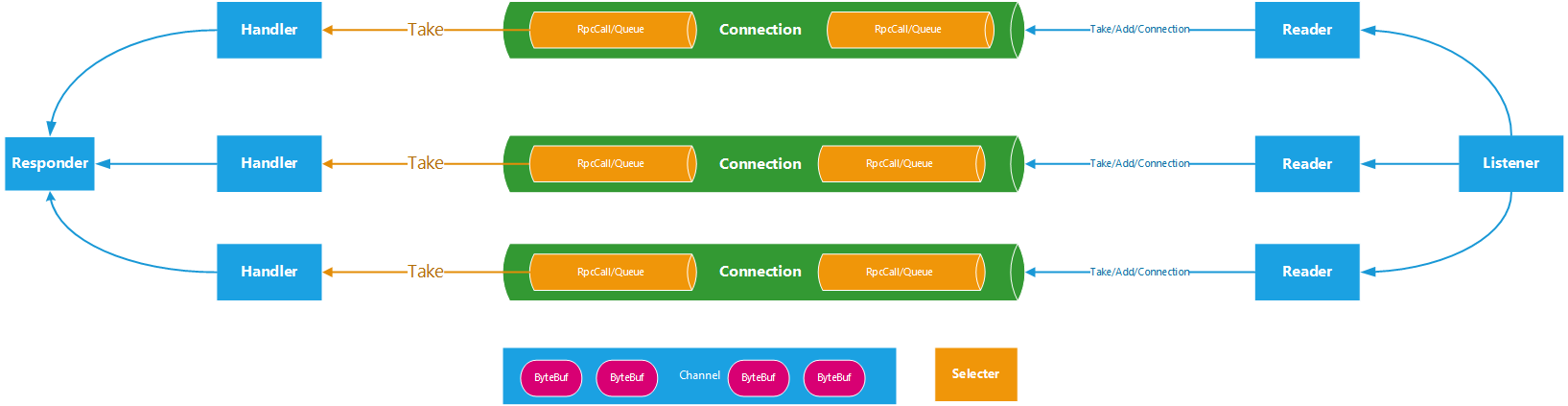
Server接收Call调用负责接收来自RPC Client的调用请求,编码成Call对象后放入到Call队列中。这一过程由Listener线程完成。具体步骤:
- Listener线程监视RPC Client发送过来的数据。
- 当有数据可以接收时,调用Connection的readAndProcess方法。
- Connection边接收边对数据进行处理,如果接收到一个完整的Call包,则构建一个Call对象PUSH到Call队列中,由Handler线程来处理Call队列中的所有Call。
Server处理Call调用负责处理Call队列中的每个调用请求,由Handler线程完成:
- Handler线程监听Call队列,如果Call队列非空,按FIFO规则从Call队列取出Call。
- 将Call交给RPC.Server处理。
- 借助JDK提供的Method,完成对目标方法的调用,目标方法由具体的业务逻辑实现。
- 返回响应。Server.Handler按照异步非阻塞
总结
以上为笔者总结Hadoop IPC部分原理,感兴趣的读者可以继续深入阅读,比如生产者消费者线程模型,以及NIO操作笔者都没有展开聊.希望本文对读者起到一定的帮助.
参考
- https://www.cnblogs.com/ZisZ/p/3253195.html
- http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_15d9697c00102wk9v.html
- http://hadoop.apache.org/





