前言
各大云厂商均开发了自己的云存储,比如亚马逊对象云存储,阿里云对象云存储,百度云对象存储。Hadoop为兼容外部存储,提供了存储接口.用户可以无缝的接入到Hadoop的设计存储中.譬如:后端真正的存储为云对象存储,但是用户输入的存储路径依然遵循HDFS API规范。本文以腾讯云对象存储为例,介绍其使用的方式。
使用COS后端存储
##### 配置COS为默认存储类
- core-site.xml
<property> <name>fs.defaultFS</name> <value>cosn://<bucket-appid></value> <description>文件访问不加cosn://,默认访问腾讯云对象存储。</description> </property> <property> <name>fs.cosn.bucket.region</name> <value>ap-xxx</value> <description>region区域</decription> </property> <property> <name>fs.cosn.userinfo.secretId</name> <value>xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx</value> <description>用户的secretId</description> </property> <property> <name>fs.cosn.userinfo.secretKey</name> <value>xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx</value> <description>用户的Secret Key</description> </property> <property> <name>fs.cosn.impl</name> <value>org.apache.hadoop.fs.cosn.CosNFileSystem</value> <description>默认文件系统实现类</description> </property> <property> <name>fs.AbstractFileSystem.cosn.impl</name> <value>org.apache.hadoop.fs.cos.CosN</value> <description>Yarn提交任务默认的CosN</description> </property>
### 使用
- 命令行访问文件系统
hadoop fs -ls -R cosn://bucket-appid/<path> - 命令行提交MR任务
bin/hadoop jar share/hadoop/mapreduce/hadoop-mapreduce-examples-x.x.x.jar wordcount /mr/input.txt /mr/output
核心流程
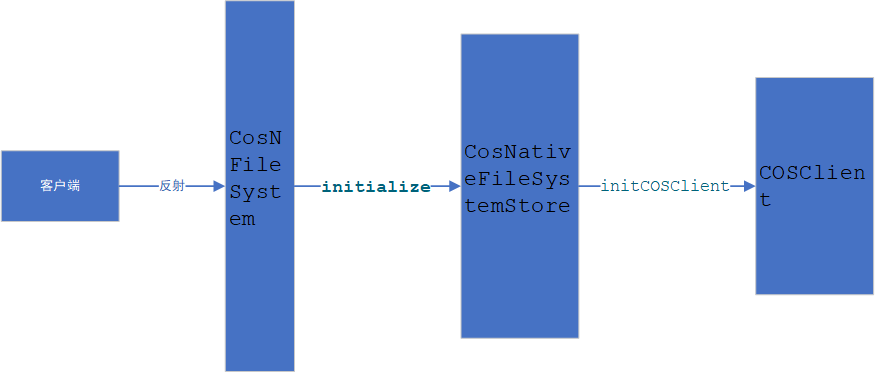
客户端访问hadoop api时,hadoop通过反射,调用用户自定义实现类(继承自FileSystem),同时调用initialize,用户自定义CosNFileSystem类后将initialize方法执行过程一直向下传递。直到调用COSClient方法。流程图如下:
核心源码分析
- CosNFileSystem.java类
public class CosNFileSystem extends FileSystem { // 获取scheme @Override public String getScheme() { return CosNFileSystem.SCHEME; } //执行initialize @Override public void initialize(URI name, Configuration conf) throws IOException { super.initialize(name, conf); this.bucket = name.getHost(); if (this.store == null) { this.store = createDefaultStore(conf); } this.store.initialize(name, conf); setConf(conf); this.uri = URI.create(name.getScheme() + "://" + name.getAuthority()); this.workingDir = new Path("/user", System.getProperty("user.name")).makeQualified( this.uri, this.getWorkingDirectory()); } //读取文件 @Override public FSDataInputStream open(Path f, int bufferSize) throws IOException { FileStatus fs = getFileStatus(f); // will throw if the file doesn't // exist if (fs.isDirectory()) { throw new FileNotFoundException("'" + f + "' is a directory"); } LOG.info("Open the file: [{}] for reading.", f); Path absolutePath = makeAbsolute(f); String key = pathToKey(absolutePath); long fileSize = store.getFileLength(key); return new FSDataInputStream(new BufferedFSInputStream( new CosNInputStream(this.getConf(), store, statistics, key, fileSize, this.boundedIOThreadPool), bufferSize)); } - CosNativeFileSystemStore
class CosNativeFileSystemStore implements NativeFileSystemStore { private COSClient cosClient; private String bucketName; private int maxRetryTimes; //创建COSClient对象 @Override public void initialize(URI uri, Configuration conf) throws IOException { try { initCOSClient(uri, conf); this.bucketName = uri.getHost(); } catch (Exception e) { handleException(e, ""); } }触类旁通
基于以上的设计方式,我们可以定义自己的FileSystem,对接自己的存储,譬如后端有FastDFS,但是其不支持Hadoop存储协议,我们可以对其API接口进行包装。然后对外提供服务。
总结
以上对腾讯云对象存储在Hadoop文件系统中的实现,希望可以对读者起到帮助作用.
参考
- http://hadoop.apache.org





